What Are Whiteflies?
Whiteflies are soft-bodied, winged insects closely related to aphids and mealybugs. Despite their name, whiteflies are not a type of fly, though they do have wings and are capable of flying.
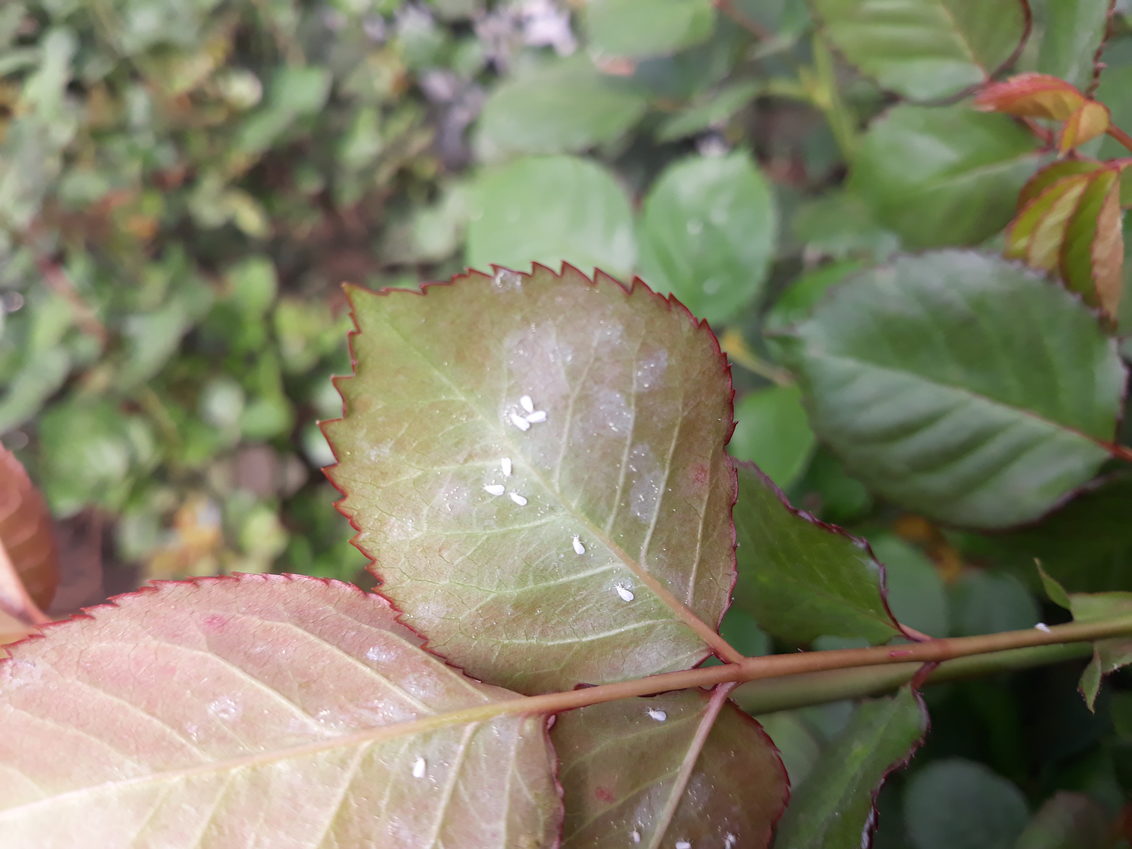
Whiteflies can be as small as 1/12 of an inch, are somewhat triangular in shape, and are often found in clusters on the undersides of leaves. They are active during the day and will scatter when disturbed, so they can be easier to spot than some nocturnal insect pests.
There are hundreds of species of whiteflies, but most affect only a small number of host plants. However, there are a few whitefly species that affect a wider range of plants, which makes them the most problematic in horticulture. These whitefly species include the greenhouse whitefly, banded winged whitefly, giant whitefly, and silver leaf whitefly, among others. Silverleaf whiteflies are slightly smaller and more yellow than other whiteflies.
How to Identify Whiteflies
Like aphids, whiteflies use their piercing mouthparts to suck up plant juices and, in turn, produce a sticky substance known as honeydew. Honeydew left on its own can cause fungal diseases such as sooty mold to form on leaves.
With heavy whitefly feeding, plants will quickly become extremely weak and may be unable to carry out photosynthesis. Leaves will wilt, turn pale or yellow, growth will be stunted, and eventually leaves may shrivel and drop off the plant.
Honeydew is a sign that the whiteflies have been feeding for several days. You might also see ants, which are attracted to the sweet honeydew.
Use the insecticides below to get rid of whiteflies.
Both adult whiteflies and larvae feed on plant phloem by injecting enzymes and removing the sap, reducing vigour of the plant, or in cases of severe infestation, killing the host. The impact of direct feeding and honeydew extreta that favours sooty mould production on leaves of infested plants affects crop yield and product aesthetic quality, reducing marketability. The most obvious whitefly feeding damage symptoms are stem blanching, chlorotic spots, leaf yellowing and shedding. In many crops, the damage caused by whitefly can be indirect, i.e. by transmitting disease-causing viruses.

Management
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) programmes are essential; including scouting, sanitation, insect exclusion nets, biological control and use of insecticides.
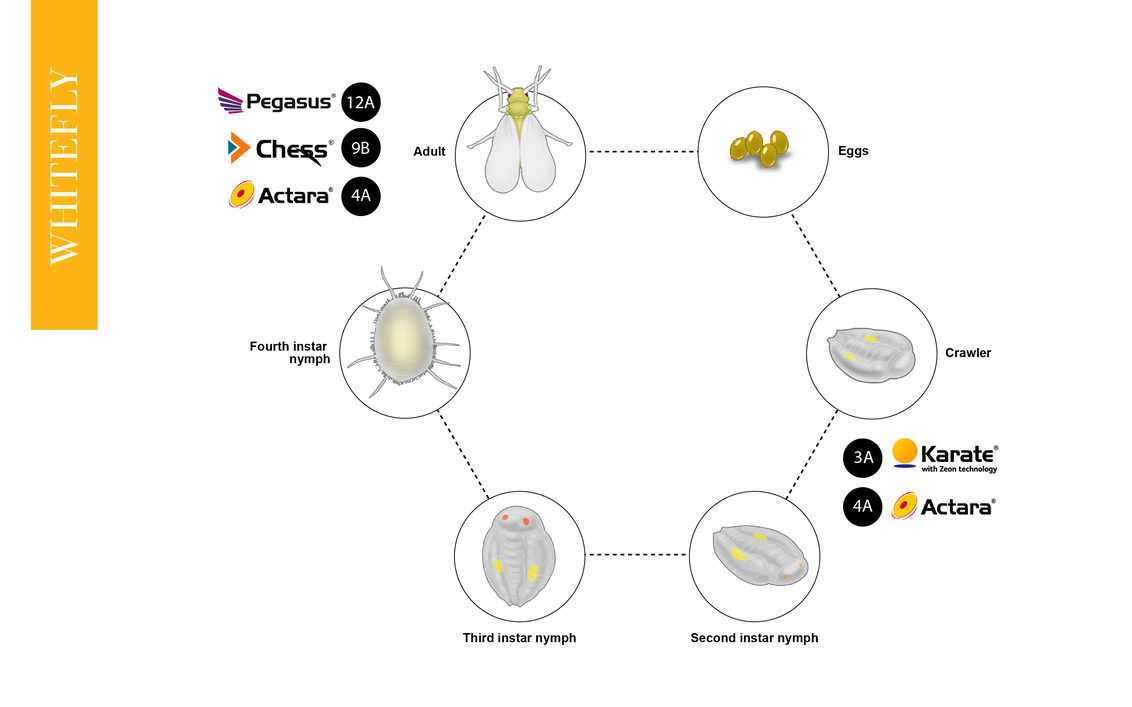
Whitefly Life Cycle
Understanding a disease’s life cycle is vital to maintaining control of your crops. Below is the whitefly life cycle, to help you get maximum control, the best products from our range have been incorporated.